Understanding Jacob Syndrome (XYY): Genetic Characteristics, Effects, and Support
Introduction:
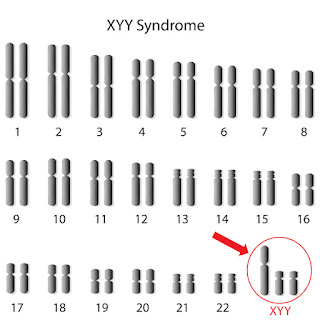
Jacob syndrome, also known as XYY syndrome, is a chromosomal condition that affects males. It is characterized by the presence of an extra Y chromosome, resulting in a karyotype of 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. In this article, we will explore the genetic characteristics of Jacob syndrome, its potential effects on individuals, and available support strategies for those living with this condition.
Causes of Jacob Syndrome:
Jacob syndrome occurs when an individual has an extra copy of the Y chromosome, resulting in a karyotype of 47,XYY. Typically, males have one X and one Y chromosome (46,XY), but individuals with Jacob syndrome have an additional Y chromosome. The extra Y chromosome in Jacob syndrome arises from a random error during sperm production. It is important to note that Jacob syndrome is not inherited and occurs spontaneously.
Symptoms and Effects:
Jacob syndrome can vary in its effects on individuals, and not all individuals with XYY will experience noticeable symptoms.
However, some common characteristics and effects associated with Jacob syndrome include:
-
Physical Features:
Individuals with Jacob syndrome may have slightly taller stature compared to their peers. However, the height difference is usually within the normal range and not significant. -
Developmental Delays:
Some individuals with Jacob syndrome may experience delays in language and speech development during early childhood. However, with appropriate intervention and support, these delays can often be addressed effectively. -
Learning and Behavioral Differences:
While not all individuals with Jacob syndrome experience learning or behavioral difficulties, some may exhibit challenges in specific areas such as reading, writing, and mathematics. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are conditions that may coexist with Jacob syndrome, but not all individuals will have these diagnoses.
Support Strategies for Individuals with Jacob Syndrome:
-
Early Intervention:
Early intervention programs that focus on speech and language development can be beneficial for individuals with Jacob syndrome who experience delays in these areas. Occupational therapy, educational support, and individualized learning plans can help address any learning challenges that may arise. -
Educational Support:
Providing a supportive and inclusive learning environment is essential for individuals with Jacob syndrome. Teachers and educators can implement tailored teaching strategies, accommodations, and assistive technologies to meet the specific learning needs of each individual. -
Psychological Support:
It is crucial to provide psychological support to individuals with Jacob syndrome and their families. Counseling, therapy, and support groups can offer guidance, coping strategies, and emotional support throughout the lifespan.
Conclusion:
Jacob syndrome, or XYY syndrome, is a chromosomal condition characterized by the presence of an extra Y chromosome in males. While it can present unique challenges in terms of development and learning, with appropriate support and interventions, individuals with Jacob syndrome can lead fulfilling lives and achieve their full potential. By raising awareness, promoting inclusivity, and providing comprehensive support, we can contribute to a more understanding and inclusive society for individuals with Jacob syndrome and other chromosomal conditions.
Comments
Post a Comment